How to operate a drone unveils the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of drone operation, from assembling the components and performing pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, battery management, and even delve into the art of capturing stunning aerial photography and videography.
Prepare to take flight!
This detailed exploration covers all aspects of drone piloting, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to safely and effectively operate your own drone. From understanding the fundamental components to mastering advanced maneuvers and ensuring safe practices, this guide is your complete handbook for successful drone operation.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section will detail the function and importance of key drone components, as well as the differences between various battery types and a step-by-step guide for drone assembly.
Drone Component Overview
The following table Artikels the major components of a typical drone and their respective functions and importance:
| Component Name | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust and lift, enabling flight. | Essential for flight; different propeller sizes and designs affect flight characteristics. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing the power for flight. | Provide the force for propulsion; motor performance impacts flight speed and stability. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; receives signals from the remote and sensors, controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. | Critical for stable flight and responsiveness to pilot input. |
| Battery | Provides power to the motors and other electronic components. | Determines flight time and overall performance; battery health is crucial for safe operation. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for autonomous flight modes and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Essential for features such as autonomous flight and precise positioning. |
| IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) | Measures the drone’s orientation and movement in three dimensions. | Critical for maintaining stability and responsiveness, especially in GPS-denied environments. |
| ESC (Electronic Speed Controller) | Controls the speed of each motor individually, allowing for precise maneuvering. | Enables precise control over motor speed and direction, crucial for stable flight. |
| Radio Receiver | Receives signals from the remote controller, translating them into commands for the flight controller. | Facilitates communication between the pilot and the drone. |
| Camera (if applicable) | Captures photos and videos. | Allows for aerial photography and videography. |
Drone Battery Types
Two common types of drone batteries are Lithium Polymer (LiPo) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). LiPo batteries offer higher energy density, resulting in longer flight times but are more susceptible to damage from overcharging or improper handling. LiFePO4 batteries are safer, have a longer lifespan, and are less prone to damage, but generally offer shorter flight times compared to LiPo batteries of similar size and weight.
Drone Assembly
Assembling a drone involves carefully connecting each component. Always refer to your drone’s specific manual for detailed instructions, as assembly procedures vary depending on the model.
- Attach the motors to the drone frame, ensuring proper alignment and secure fastening.
- Connect the ESCs to the motors and the flight controller.
- Install the propellers onto the motors, ensuring correct orientation.
- Connect the battery to the power distribution board and flight controller.
- Mount the GPS module and other necessary sensors.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and sensors using the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Perform a pre-flight check to ensure everything is correctly assembled and functioning.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is essential to ensure the drone’s safe and reliable operation. This involves inspecting various components and calibrating the drone’s systems. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect the propellers for damage or cracks.
- Check the motor mounts for tightness and security.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Verify that all connections are secure and free from damage.
- Check the GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Inspect the surrounding area for obstacles and potential hazards.
- Check the weather conditions; avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Review relevant local drone regulations and airspace restrictions.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and sensors is crucial for accurate flight and stability. The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model, but generally involves following the instructions provided in the drone’s manual. This typically involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern while the calibration process runs on the controller.
Weather Conditions and Flight Safety
Adverse weather conditions can significantly impact drone operation. Strong winds can cause loss of control, while rain or snow can damage the drone’s electronics. Always check the weather forecast before flying and avoid flying in conditions that could compromise safety.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents and damage to the drone. Understanding different takeoff/landing modes and maintaining a safe distance from obstacles are essential for successful flights.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
A typical safe takeoff involves engaging an assisted takeoff mode (if available) which helps maintain stability during ascent. This mode often utilizes GPS and IMU data to help the drone ascend smoothly. Landing should be performed gradually and carefully, allowing the drone to gently settle to the ground. Avoid abrupt landings, which can damage the drone’s components.
Obstacle Avoidance During Takeoff and Landing, How to operate a drone
Maintaining a safe distance from obstacles during takeoff and landing is paramount. Ensure a clear area around the drone to prevent collisions. This is particularly important in confined spaces or areas with numerous obstacles.
Potential Issues During Takeoff and Landing
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Drone drifts during takeoff | Check for wind conditions and calibrate the compass and IMU. Consider using an assisted takeoff mode. |
| Abrupt landing | Reduce descent rate, ensure sufficient battery power, and avoid sudden movements of the controller. |
| Collision with obstacle | Ensure a clear area around the drone during takeoff and landing. Use obstacle avoidance features if available. |
| Loss of GPS signal | Fly in an open area with a strong GPS signal. Avoid flying near tall buildings or other structures that may interfere with the signal. |
Controlling the Drone in Flight
Understanding the functions of the drone remote’s controls is essential for safe and effective flight. This section will detail the functions of typical controls and how to maneuver the drone in various directions.
Drone Remote Control Functions
- Left Stick (Yaw and Throttle): Controls the drone’s rotation (yaw) and altitude (throttle).
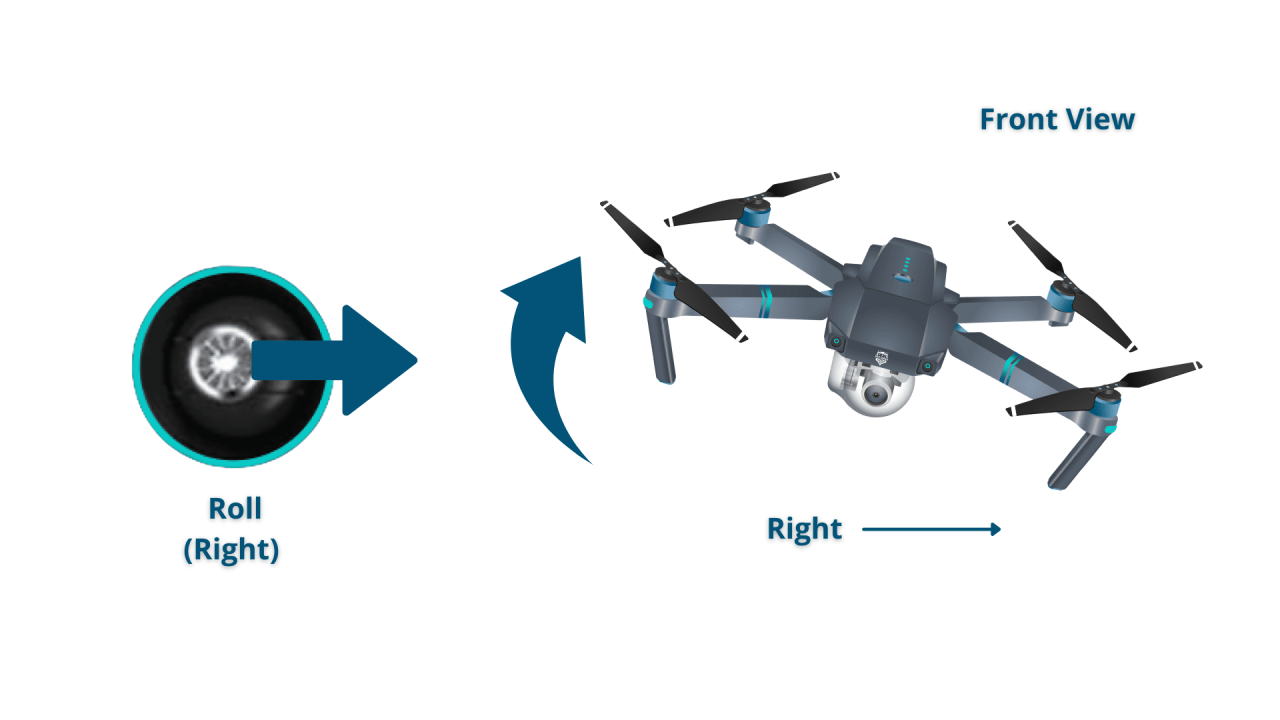
- Right Stick (Pitch and Roll): Controls the drone’s forward/backward (pitch) and left/right (roll) movement.
- Buttons and Switches: Various buttons and switches control features like camera operation, flight modes, Return-to-Home (RTH), and emergency stops.
Drone Maneuvering
The drone is maneuvered using the two sticks on the remote controller. The left stick controls altitude and rotation, while the right stick controls forward/backward and left/right movement. Smooth and controlled movements are key to maintaining stability and avoiding accidents.
Maintaining a Stable Hover
Hovering requires precise control of the throttle and maintaining a neutral position on the pitch and roll sticks. Practice is crucial to master this skill, as it’s fundamental to many aerial maneuvers.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Beyond basic flight control, drones offer various flight modes and advanced techniques for more complex maneuvers. Understanding these modes and techniques opens up a wider range of possibilities for drone operation.
Drone Flight Modes
| Flight Mode | Description | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Utilizes GPS data for stable flight and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Ideal for stable, autonomous flight and precise positioning. |
| Attitude Mode | Relies on the IMU for orientation and stability, independent of GPS. | Suitable for indoor flying or areas with weak GPS signals. |
| Manual Mode | Provides direct control over the drone’s motors, offering maximum maneuverability but requiring significant skill. | Used for advanced maneuvers and precise control. |
Basic Aerial Maneuvers
Orbiting a point of interest involves maintaining a constant distance and altitude while circling the subject. This requires smooth and coordinated control of the drone’s movement.
Waypoints and Flight Planning
Waypoints are pre-programmed points in a drone’s flight path. They can be used to create complex flight plans, allowing for automated sequences of movements. Many drone apps and software provide tools for creating and managing waypoints.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Drone operation involves potential hazards, and adherence to safety precautions and regulations is crucial for responsible flying. This section will Artikel key safety measures and relevant regulations.
Drone Safety Precautions

- Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
- Avoid flying near people, animals, or buildings.
- Check the battery level before and during flight.
- Be aware of airspace restrictions and regulations.
- Never fly in adverse weather conditions.
- Regularly inspect the drone for damage or wear.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Drone regulations vary by country and region. It’s essential to research and understand the specific rules and restrictions in your area before flying. These regulations often include limitations on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and specific locations where drone operation is prohibited.
Drone Safety Plan
A comprehensive safety plan should include pre-flight checks, emergency procedures (such as battery failure or loss of control), and post-flight inspection. This plan should also detail communication protocols and contingency plans for unexpected events.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is key to producing high-quality aerial media.
Camera Settings Optimization

Adjusting aperture, shutter speed, and ISO affects image quality. A wider aperture (lower f-stop) allows more light, resulting in a shallower depth of field. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur. ISO affects image sensitivity to light; higher ISO values are needed in low-light conditions but can increase noise.
Camera Angles and Composition
Different camera angles and compositions can significantly impact the visual appeal of aerial shots. Experiment with various angles and perspectives to find the most effective way to capture your subject.
Drone Photography and Videography Shoot Planning
- Plan the shot: Determine the location, time of day, and desired angles.
- Check weather conditions and airspace restrictions.
- Prepare the drone and camera settings.
- Perform a test flight to ensure everything is working correctly.
- Capture the footage, paying attention to composition and lighting.
- Review and edit the footage.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Despite careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. This section Artikels solutions for common problems and steps to take if a drone malfunctions mid-flight.
Solutions for Common Drone Problems
- Low battery warning: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS signal loss: Fly in an open area with a strong GPS signal. Avoid flying near tall buildings or other structures that may interfere with the signal.
- Motor malfunction: Inspect the motor and ESC for damage. If necessary, replace the faulty component.
- Propeller damage: Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- Flight controller issues: Recalibrate the flight controller or seek professional assistance.
Drone Malfunction Mid-Flight
If a drone malfunctions mid-flight, prioritize safety. Attempt to regain control if possible, but if the situation is unsafe, initiate an emergency landing procedure (if available) or bring the drone down as safely as possible. Assess the damage after landing and take appropriate action.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including cleaning the propellers and inspecting the drone’s components for damage, can help prevent future issues and extend the drone’s lifespan.
Drone Battery Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance of drone batteries are crucial for maximizing their lifespan and ensuring safe operation. This section details the proper charging and storage techniques, and how to identify a damaged battery.
Charging and Storing Drone Batteries
Always charge LiPo batteries using a suitable charger, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid overcharging or discharging the batteries completely. Store LiPo batteries in a cool, dry place, away from flammable materials, at a partially charged state (around 30-50%). LiFePO4 batteries are less sensitive to overcharging and discharging but still benefit from similar storage practices.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires a solid grasp of the fundamentals, and a great resource for learning this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone found at DroneFair. After familiarizing yourself with this guide, practice is crucial to becoming proficient and confident in handling your drone safely and effectively.
Signs of Damaged or Failing Battery
Signs of a damaged or failing battery include swelling, unusual heat generation during charging or use, decreased flight time, and inconsistent performance. If any of these signs are observed, replace the battery immediately.
Battery Charging Methods
Several methods exist for charging drone batteries, including parallel charging (charging multiple batteries simultaneously) and individual charging. The choice of method depends on the charger and the number of batteries to be charged. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific charger and battery type.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible and skillful operation ensures both successful flights and the safety of yourself and others.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding experience that opens up a world of possibilities. By understanding the fundamentals, adhering to safety protocols, and continuously practicing, you can confidently navigate the skies and capture breathtaking aerial perspectives. Remember, responsible drone operation is paramount, ensuring both your safety and the safety of those around you. Soar safely and enjoy the flight!
Questions and Answers
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for drones with obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and battery size. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge, but always check the manufacturer’s specifications.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to manual mode and carefully bring it down to a safe landing area. Avoid flying in areas with poor GPS reception.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or if you notice erratic behavior during flight.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local civil aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and airspace restrictions in your area. The FAA (in the US) and equivalent agencies in other countries provide comprehensive information.
